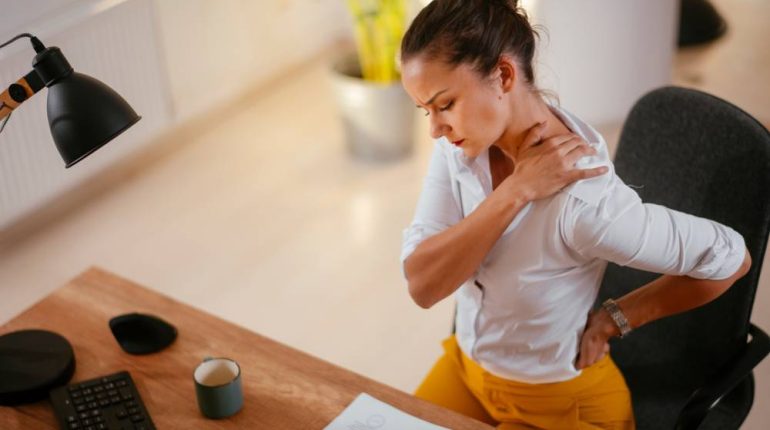
Arthritis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, affects millions of people worldwide. While it is commonly associated with older adults, arthritis can also affect young people, including children and teenagers. Understanding how to manage arthritis effectively is crucial for improving the quality of life for both young and old individuals. This article explores various strategies and treatments to control arthritis, offering valuable information for those affected by this condition.
Understanding Arthritis
Arthritis is not a single disease but a term that covers over 100 different types of joint-related conditions. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Osteoarthritis results from wear and tear on the joints, often due to aging or repetitive stress. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Common symptoms of arthritis include:
Joint pain
Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
Swelling around the joints
Reduced range of motion
Redness and warmth in the affected areas
These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
Managing Arthritis in Young People
Managing arthritis in young people requires a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and support. Here are some effective strategies:
Early Diagnosis and Treatment:
Early diagnosis is critical for managing arthritis in young people. Prompt medical attention can help slow the progression of the disease and prevent long-term joint damage.
Medications:
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications help reduce pain and inflammation.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Used primarily for RA, these drugs slow disease progression.
Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy helps maintain joint function and flexibility. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen muscles around the joints and improve mobility.

Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help manage arthritis symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit those with arthritis.
Regular Exercise:
Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking are beneficial for maintaining joint health without putting too much stress on the joints. Exercise also helps control weight, reducing pressure on weight-bearing joints.
Support Systems:
Support from family, friends, and support groups can help young people cope with the emotional challenges of living with arthritis. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide comfort and practical advice.
Managing Arthritis in Older Adults
For older adults, managing arthritis involves similar strategies, with additional considerations for age-related factors. Here are key approaches:
Medications:
Older adults may require a combination of medications to manage pain and inflammation. It’s important to regularly review medications with a healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects and interactions.
Physical Activity:
Staying active is crucial for managing arthritis in older adults. Gentle exercises such as tai chi, yoga, and water aerobics can improve flexibility, strength, and balance. Regular movement also helps prevent joint stiffness.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on joints, particularly the knees and hips. Weight loss can significantly reduce pain and improve mobility in individuals with osteoarthritis.
Assistive Devices:
Devices such as canes, walkers, and joint braces can provide support and reduce joint strain. Occupational therapists can recommend appropriate assistive devices and teach proper use.
Joint Care:
Protecting the joints from further damage is essential. Older adults should avoid activities that put excessive stress on the joints and use ergonomic tools to minimize strain during daily tasks.
Alternative Therapies:
Some older adults find relief from arthritis symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care. These therapies can complement conventional treatments and provide additional pain relief.
Lifestyle Modifications for All Ages
Certain lifestyle modifications can benefit individuals of all ages in managing arthritis:
Healthy Eating:
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish, can help reduce inflammation and pain. Avoiding processed foods, sugar, and excessive salt is also beneficial.
Hydration:
Staying well-hydrated helps maintain joint lubrication and overall health. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential.
Stress Management:
Stress can exacerbate arthritis symptoms. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Adequate Sleep:
Quality sleep is vital for managing arthritis. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help improve sleep quality.
Smoking Cessation:
Smoking can worsen arthritis symptoms and interfere with the effectiveness of certain medications. Quitting smoking can lead to significant improvements in joint health.
Managing arthritis in both young and old individuals requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and support systems. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing long-term joint damage and improving quality of life. By incorporating healthy habits, staying active, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals with arthritis can effectively manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. If you or someone you know is struggling with arthritis, consider exploring the various strategies and treatments available to take control of this condition.