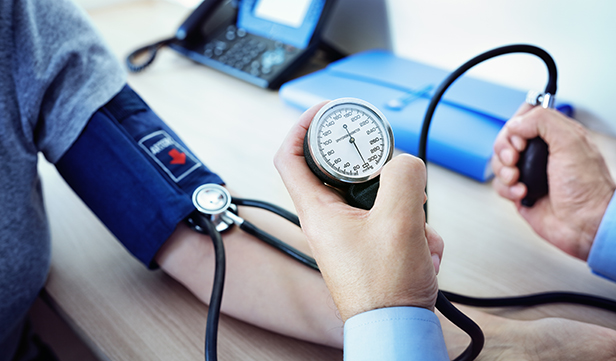
In a recent development concerning cardiovascular health, new guidelines have been released emphasizing the critical role of blood pressure management in preventing heart-related complications. With heart disease remaining a leading cause of death worldwide, these guidelines aim to provide essential information and strategies for individuals to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
The guidelines, issued by prominent health organizations including the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American College of Cardiology (ACC), underscore the significance of monitoring and controlling blood pressure to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. According to the latest recommendations, optimal blood pressure levels are defined as less than 120/80 mm Hg, with elevated blood pressure categorized between 120-129/80 mm Hg.
One of the key highlights of the guidelines is the emphasis on lifestyle modifications as the first line of defense against high blood pressure. These modifications include adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting sodium intake. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, is also encouraged as it helps lower blood pressure and improves overall cardiovascular fitness.
Furthermore, the guidelines stress the importance of weight management, as excess weight can contribute to elevated blood pressure levels. Individuals are advised to strive for a healthy body weight through a combination of balanced nutrition and regular exercise. Smoking cessation is another crucial aspect highlighted in the guidelines, as tobacco use significantly increases the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
For individuals with elevated blood pressure or hypertension, pharmacological interventions may be necessary to achieve optimal blood pressure control. Healthcare providers may prescribe medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers, depending on the patient’s specific health profile and risk factors.
Importantly, the guidelines emphasize the need for personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s unique health status and preferences. Regular monitoring of blood pressure levels is recommended to track progress and ensure the effectiveness of treatment strategies.
In addition to pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications remain essential components of hypertension management even for individuals on medication. Compliance with medication regimens, adherence to dietary recommendations, and commitment to regular physical activity are vital for long-term blood pressure control and overall cardiovascular health.
Education and awareness initiatives are crucial in empowering individuals to take proactive steps in managing their blood pressure. Public health campaigns, community outreach programs, and educational resources play a significant role in promoting heart-healthy behaviors and reducing the burden of cardiovascular disease on a global scale.
In summary, the release of updated guidelines underscores the critical importance of blood pressure management in safeguarding heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. By implementing lifestyle modifications, adhering to prescribed medications, and regularly monitoring blood pressure levels, individuals can take proactive measures to protect themselves against the devastating effects of hypertension and heart disease. With concerted efforts from healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public, significant strides can be made towards achieving better cardiovascular outcomes for all.