The human body is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiome. These tiny inhabitants, primarily bacteria, reside in various parts of the body, with the gut hosting the majority. The microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining health and well-being, influencing everything from digestion to immunity. This article explores the fascinating world of the microbiome, its impact on health, and ways to nurture a healthy gut.
What is the Microbiome?
The microbiome consists of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that live in and on our bodies. The gut microbiome, located in the intestines, is the most studied and has the most significant impact on health. Each person’s microbiome is unique, shaped by factors such as genetics, diet, environment, and lifestyle.
The Role of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome performs several essential functions:
Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: Gut bacteria help break down complex carbohydrates, fibers, and proteins, aiding in digestion and nutrient absorption. They produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are vital for colon health and provide energy for the body.
Immune System Support: A significant portion of the immune system is located in the gut. The microbiome helps train the immune system to distinguish between harmful pathogens and harmless substances, preventing autoimmune reactions and infections.
Metabolism Regulation: Gut bacteria influence metabolic processes, affecting how the body stores fat, maintains blood sugar levels, and regulates appetite. An imbalance in the microbiome can contribute to metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes.
Mental Health and Brain Function: The gut-brain axis refers to the communication network linking the gut and the brain. Gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which influence mood, stress response, and cognitive function. A healthy microbiome is associated with better mental health and reduced risk of conditions like depression and anxiety.
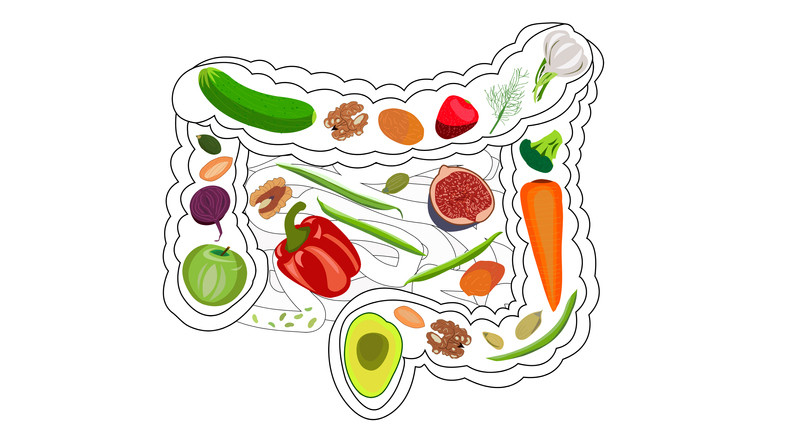
Factors Affecting the Microbiome
Several factors can influence the composition and health of the microbiome:
Diet: The food we eat has a profound impact on the microbiome. Diets high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods promote a diverse and healthy microbiome. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can harm gut bacteria.
Antibiotics: While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, they can also disrupt the microbiome by killing beneficial bacteria. It’s crucial to use antibiotics only when necessary and follow a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Lifestyle Factors: Stress, lack of sleep, and sedentary behavior can negatively affect the microbiome. Healthy lifestyle habits, including regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management, support a balanced microbiome.
Environmental Exposures: Environmental factors such as pollution, chemicals, and hygiene practices can impact the microbiome. Overuse of sanitizers and antibiotics can reduce microbial diversity.
Nurturing a Healthy Microbiome
Maintaining a healthy microbiome is crucial for overall health. Here are some tips to nurture your gut bacteria:
Eat a Diverse Diet: Consuming a variety of foods, especially plant-based ones, promotes a diverse microbiome. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds in your diet.
Include Fermented Foods: Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut health.
Consume Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria. Foods rich in prebiotics include garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, and oats.
Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods, high in sugar and unhealthy fats, can negatively impact the microbiome. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut lining.
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the microbiome. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and mindfulness.
Get Enough Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for a healthy microbiome. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
Use Antibiotics Wisely: Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare provider. Discuss the need for antibiotics and consider taking probiotics during and after antibiotic treatment to support the microbiome.
Avoid Over-Sanitizing: While hygiene is important, excessive use of sanitizers and antibacterial products can reduce microbial diversity. Use these products judiciously.
The Future of Microbiome Research
The study of the microbiome is a rapidly evolving field with exciting potential. Future research may lead to personalized microbiome therapies, probiotics tailored to individual needs, and new treatments for various health conditions. Understanding the microbiome’s role in health could revolutionize medicine and lead to more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
The microbiome is a vital component of health, influencing digestion, immunity, metabolism, and even mental well-being. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and prudent use of antibiotics, you can nurture a thriving microbiome. As research continues to uncover the microbiome’s mysteries, the potential for improving health and preventing disease through microbiome management becomes increasingly promising. Embrace the power of your gut bacteria and take steps today to support your microbiome for a healthier tomorrow.