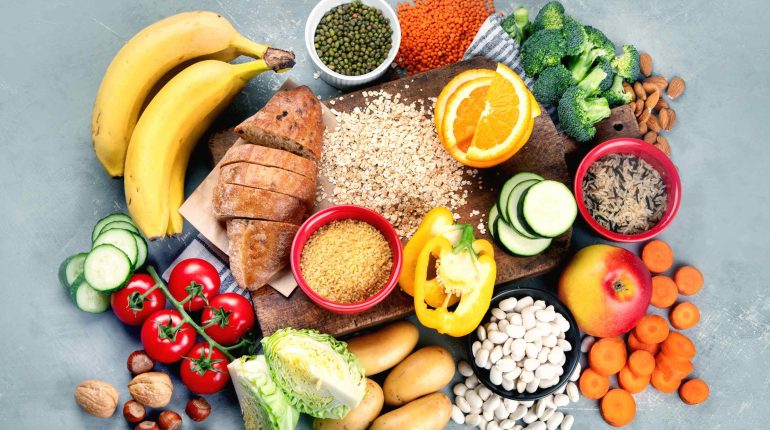
In the world of nutrition, macronutrients are fundamental components that our bodies require in large amounts to function properly. Understanding macronutrients and how they contribute to our health can help us make informed dietary choices and maintain a balanced diet. This article will delve into what macronutrients are, their types, their roles in the body, and how to incorporate them into your diet effectively.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are nutrients that our bodies need in larger quantities for energy, growth, and bodily functions. They are divided into three primary categories: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each type of macronutrient serves unique and vital roles in maintaining our health.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are found in foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products. Carbohydrates are classified into two main types: simple and complex.
Simple Carbohydrates:
These are sugars found naturally in foods like fruits and milk, as well as in processed foods such as candy and soft drinks.
Simple carbohydrates provide a quick source of energy because they are rapidly broken down by the body.
Complex Carbohydrates:
These include starches and fiber found in whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables like potatoes and corn.
Complex carbohydrates take longer to digest, providing a more sustained energy release. They are also rich in essential nutrients and fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Role of Carbohydrates:
Provide energy for daily activities and bodily functions.
Support brain function, as the brain primarily uses glucose (a simple sugar derived from carbohydrates) for energy.
Aid in the proper functioning of the digestive system through dietary fiber.
Incorporating Carbohydrates:
Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread.
Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet.
Limit the intake of refined sugars and processed foods.
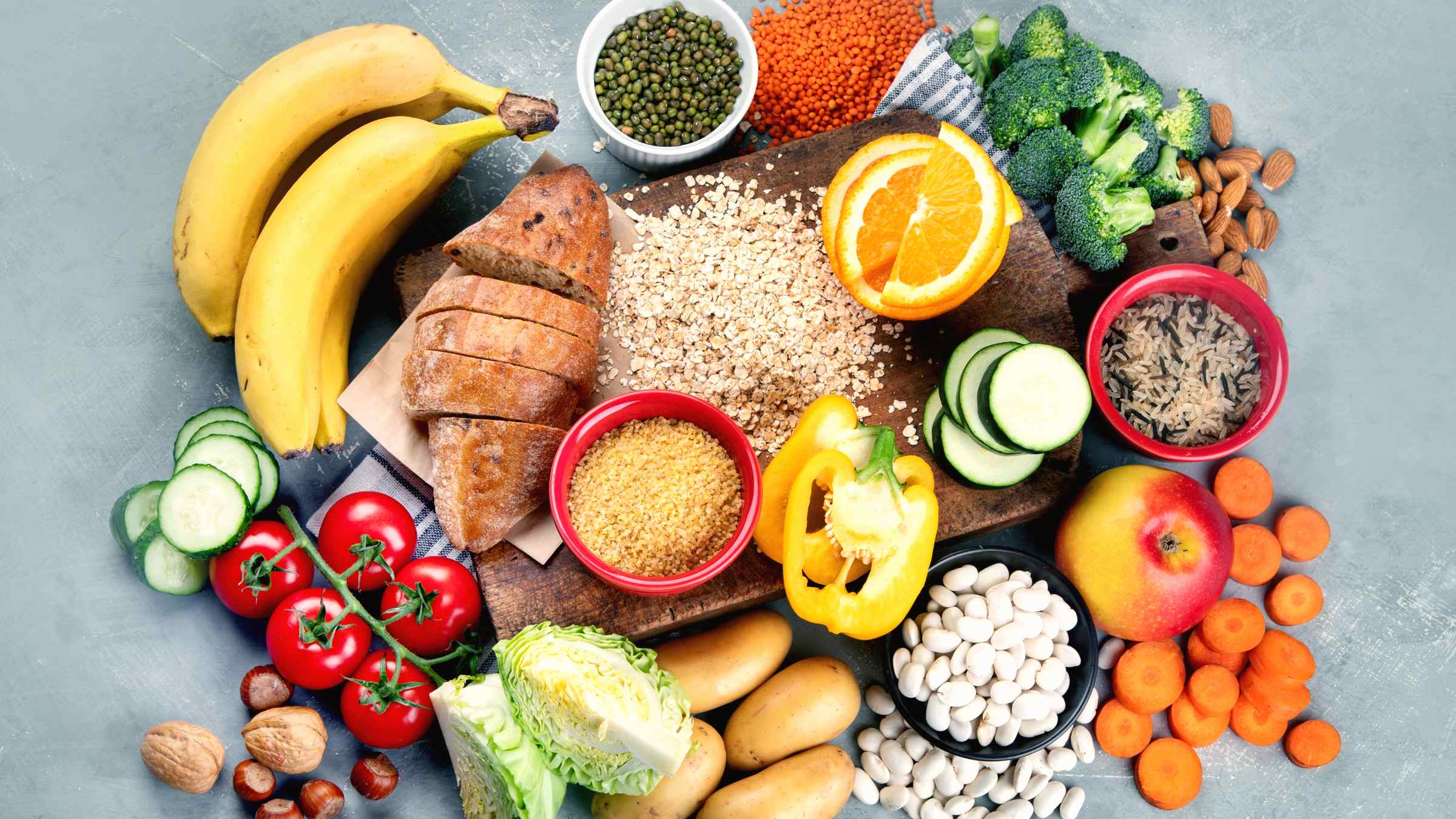

Proteins
Proteins are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They are composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body. Sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Complete Proteins:
These contain all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. Animal products like meat, fish, and dairy are complete proteins.
Incomplete Proteins:
These lack one or more essential amino acids. Most plant-based proteins fall into this category. However, by combining different plant-based proteins (e.g., rice and beans), you can obtain all essential amino acids.
Role of Proteins:
Build and repair tissues, including muscles, skin, and organs.
Produce enzymes and hormones that regulate bodily functions.
Support immune function by creating antibodies.
Incorporating Proteins:
Include a variety of protein sources in your diet, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts.
For vegetarians and vegans, combine different plant-based proteins to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
Fats
Fats are crucial for various bodily functions and should not be entirely eliminated from the diet. They are found in foods such as oils, butter, nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish. Fats are classified into three main types: saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats.
Saturated Fats:
Found in animal products like meat and dairy, as well as some plant oils (e.g., coconut oil).
While necessary in small amounts, excessive intake of saturated fats can lead to heart disease.
Unsaturated Fats:
Found in foods like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
Unsaturated fats are beneficial for heart health and can help reduce cholesterol levels.
Trans Fats:
Found in processed and fried foods.
Trans fats should be avoided as they increase the risk of heart disease and other health issues.
Role of Fats:
Provide a concentrated source of energy.
Support cell growth and protect organs.
Aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
Produce hormones and support brain health.
Incorporating Fats:
Choose healthy fats such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Limit the intake of saturated fats and avoid trans fats.
Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish and flaxseeds, to support heart health.
Balancing Macronutrients
A balanced diet includes an appropriate proportion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The ideal macronutrient ratio can vary depending on individual health goals, activity levels, and metabolic needs. However, general guidelines suggest the following distribution:
Carbohydrates: 45-65% of daily caloric intake
Proteins: 10-35% of daily caloric intake
Fats: 20-35% of daily caloric intake
Practical Tips for a Balanced Diet
Meal Planning:
Plan your meals to include a variety of macronutrients. For example, a balanced meal could include whole grains (carbohydrates), lean chicken (protein), and a salad with olive oil dressing (healthy fats).
Portion Control:
Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating any one macronutrient. Use measuring cups or a food scale if necessary.
Healthy Snacks:
Choose snacks that offer a good balance of macronutrients, such as a piece of fruit with a handful of nuts or yogurt with berries.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, as hydration is essential for overall health and can support proper digestion and metabolism.
Understanding macronutrients and their roles in the body is essential for maintaining a balanced diet and promoting overall health. By incorporating the right proportions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into your meals, you can ensure that your body gets the energy and nutrients it needs to function optimally. Making informed dietary choices and staying mindful of macronutrient intake can lead to improved health, increased energy levels, and a greater sense of well-being.