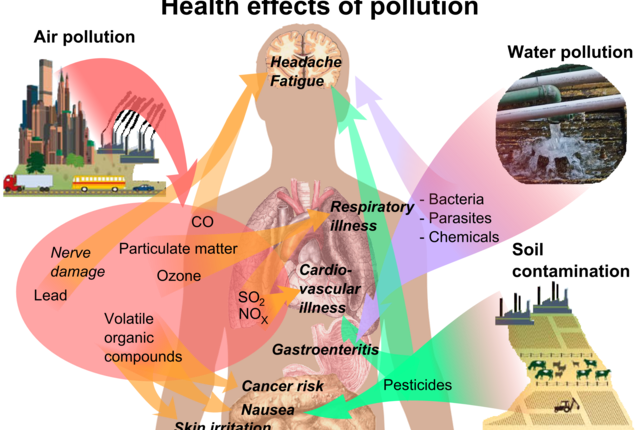
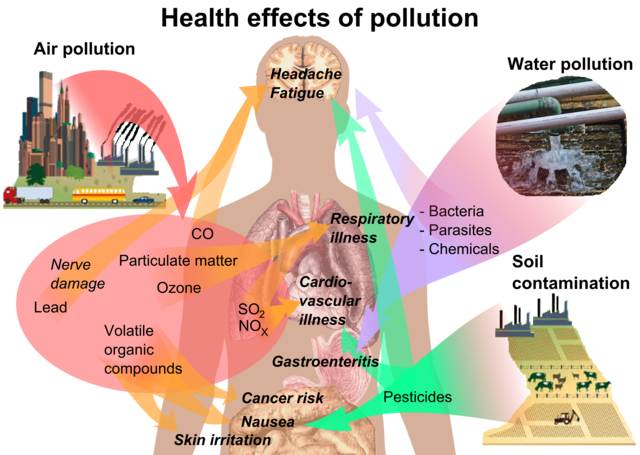
Air pollution poses significant risks to human health, with detrimental effects that extend beyond respiratory issues. Understanding these impacts is crucial for individuals and communities to take proactive measures to mitigate exposure and protect well-being.
Air pollution comprises a complex mixture of particles and gases, often emitted from various sources such as vehicles, industrial facilities, and agricultural activities. These pollutants can have immediate and long-term effects on health, impacting individuals of all ages and predisposing vulnerable populations to heightened risks.
1. **Respiratory Health**:
One of the most well-documented health effects of air pollution is its impact on respiratory health. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ground-level ozone (O3) can penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to inflammation, exacerbation of asthma and other respiratory conditions, and increased risk of respiratory infections.
2. **Cardiovascular Health**:
Air pollution is also linked to cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension. Exposure to pollutants like nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) can contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular conditions by triggering inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction.
3. **Neurological Health**:
Emerging research suggests that air pollution may have adverse effects on neurological health, including cognitive decline and neurodevelopmental disorders. Exposure to pollutants such as particulate matter and heavy metals has been associated with neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and increased risk of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
4. **Reproductive Health**:
Air pollution can also impact reproductive health, with potential effects on fertility, pregnancy outcomes, and child development. Prenatal exposure to pollutants like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and heavy metals has been linked to adverse birth outcomes, including low birth weight, preterm birth, and developmental abnormalities.
5. **Immune System**:
Air pollution can compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and reducing the body’s ability to mount an effective immune response. Prolonged exposure to pollutants can lead to chronic inflammation, immune dysregulation, and increased vulnerability to respiratory infections, including influenza and pneumonia.
6. **Long-term Health Impacts**:
Chronic exposure to air pollution is associated with a range of long-term health impacts, including reduced life expectancy, decreased lung function, and increased risk of chronic respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers. These effects underscore the importance of sustained efforts to improve air quality and protect public health.
Addressing the health effects of air pollution requires collaborative efforts at the individual, community, and policy levels. Strategies such as reducing emissions from transportation and industry, promoting cleaner energy sources, implementing green infrastructure, and advocating for stricter air quality standards can help mitigate the impact of air pollution on health.
Furthermore, individuals can take steps to reduce their personal exposure to air pollution by avoiding outdoor activities during periods of high pollution, using indoor air purifiers, maintaining good indoor ventilation, and advocating for clean air policies in their communities.
In conclusion, air pollution poses significant health risks that necessitate proactive measures to safeguard public health. By raising awareness of the health effects of air pollution and implementing effective strategies to reduce emissions and exposure, we can create healthier environments for current and future generations.